A 65-year-old man with Type 2 Diabetes develops skin masses and poor glycemic control. Discover a common but preventable complication of insulin therapy.

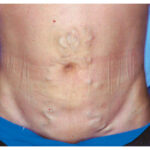
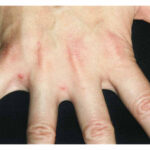
A 65-year-old man with type 2 diabetes was admitted to the hospital with hyperosmolar hyperglycemia state. Two weeks before admission, the patient’s insulin dose had been increased owing to inadequate glycemic control. The physical exam was notable for confusion and sarcopenia. There were also rubbery, subcutaneous masses on either side of the umbilicus where the patient had been repeatedly administering insulin injections. Which of the following should be done to prevent this finding?
What is the most likely diagnosis?
Diabetes Mellitus, Insulin, Lipohypertrophy, Rotating insulin injection sites, Subcutaneous Injection